Basic Git Commands with Example || Upload Folder / Project To Gitlab
Basic Git Commands with Example
git config
usage:
git config You can use it to configure the author's name, email address, file formats and many more to be used with your commits.
git init
Usage:
git config –global user.name “[name]”
Usage:
git config –global user.email “[email address]”
This command sets the author name and email address respectively to be used with your commits.
git add
Usage:
git add [file]
This command adds a file to the staging area.
git add -Astages all changesgit add .stages new files and modifications, without deletionsgit add -ustages modifications and deletions, without new files
git checkout
Usage: git checkout [branch name]
This command is used to switch from one branch to another.
Usage: git checkout -b [branch name]
This command creates a new branch and also switches to it.
git checkout [branch name] git checkout -b [branch name] git commit
Usage: git commit -m “[ Type in the commit message]”
This command records or snapshots the file permanently in the version history.
git commit -m “[ Type in the commit message]” git status
Usage: git status
This command lists all the files that have to be committed.
Usage:
git status
This command lists all the files that have to be committed.
git pull
Usage: git pull [Repository Link]
This command fetches and merges changes on the remote server to your working directory.
git pull [Repository Link] git push
Usage: git push [variable name] master
This command sends the committed changes of master branch to your remote repository.
Usage: git push [variable name] [branch]
This command sends the branch commits to your remote repository.
Usage: git push –all [variable name]
This command pushes all branches to your remote repository.
Usage: git push [variable name] :[branch name]
This command deletes a branch on your remote repository.
git merge
git push [variable name] master git push [variable name] [branch] git push –all [variable name] git push [variable name] :[branch name]
Usage: git merge [branch name]
This command merges the specified branch’s history into the current branch.
git merge [branch name] git clone
Usage:
git clone [url]
This command is used to obtain a repository from an existing URL.
git branch
Usage:
git branch
This command lists all the local branches in the current repository.
Usage:
git branch [branch name]
This command creates a new branch.
Usage:
git branch -d [branch name]
This command deletes the feature branch.
git show
Usage:
git show [commit]
This command shows the metadata and content changes of the specified commit.
git reset
Usage:
git reset [file]
This command unstages the file, but it preserves the file contents.
Usage:
git reset [commit]
This command undoes all the commits after the specified commit and preserves the changes locally.
Usage:
git reset –hard [commit]
This command discards all history and goes back to the specified commit.
git tag
Usage:
git tag [commitID]
This command is used to give tags to the specified commit.
git remote
Usage:
git remote add [variable name] [Remote Server Link]
This command is used to connect your local repository to the remote server.
Upload Folder / Project To Gitlab
GitLab is a web-based DevOps lifecycle tool that provides a Git-repository manager providing wiki, issue-tracking and continuous integration/continuous deployment pipeline features, using an open-source license, developed by GitLab Inc
You can also upload existing files from your computer using the instructions below.
Cloning a repository
On GitHub.com, navigate to the main page of the repository.
Above the list of files, click Code.
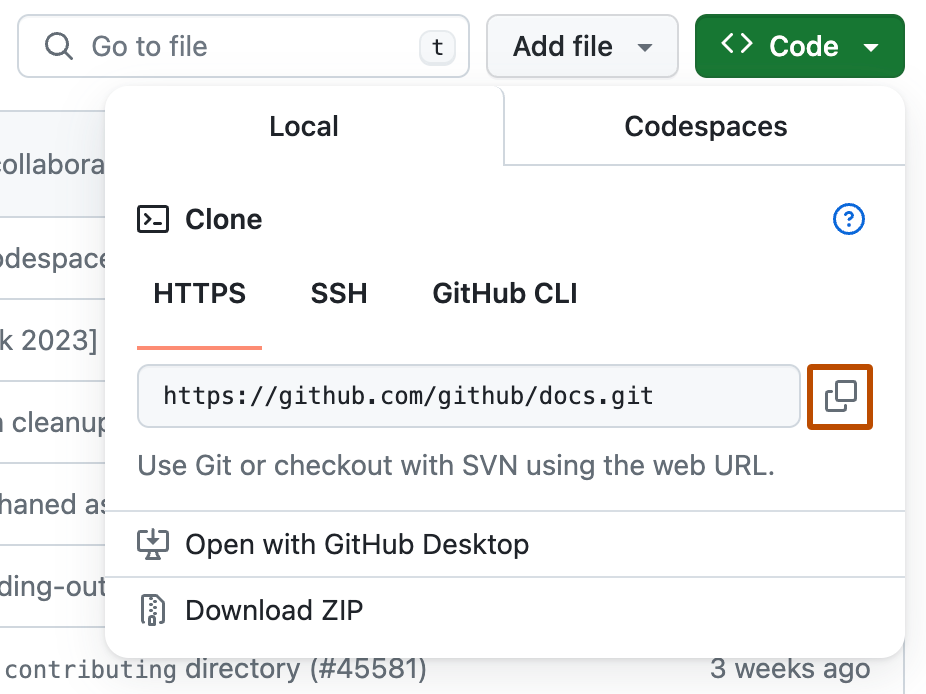
To clone the repository using HTTPS, under "Clone with HTTPS", click . To clone the repository using an SSH key, including a certificate issued by your organization's SSH certificate authority, click Use SSH, then click . To clone a repository using GitHub CLI, click Use GitHub CLI, then click .

Open Terminal.
Change the current working directory to the location where you want the cloned directory.
Type
git clone, and then paste the URL you copied earlier.$ git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/YOUR-REPOSITORYPress Enter to create your local clone.
$ git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/YOUR-REPOSITORY > Cloning into `Spoon-Knife`... > remote: Counting objects: 10, done. > remote: Compressing objects: 100% (8/8), done. > remove: Total 10 (delta 1), reused 10 (delta 1) > Unpacking objects: 100% (10/10), done.
1.git init
2.git checkout branchname
3.git add -A
4.git commit -m "note"
5.git pull origin master
6.git push origin branchname
7.git checkout master
8.git merge branchname
9.git push origin master
10.git checkout branchname


